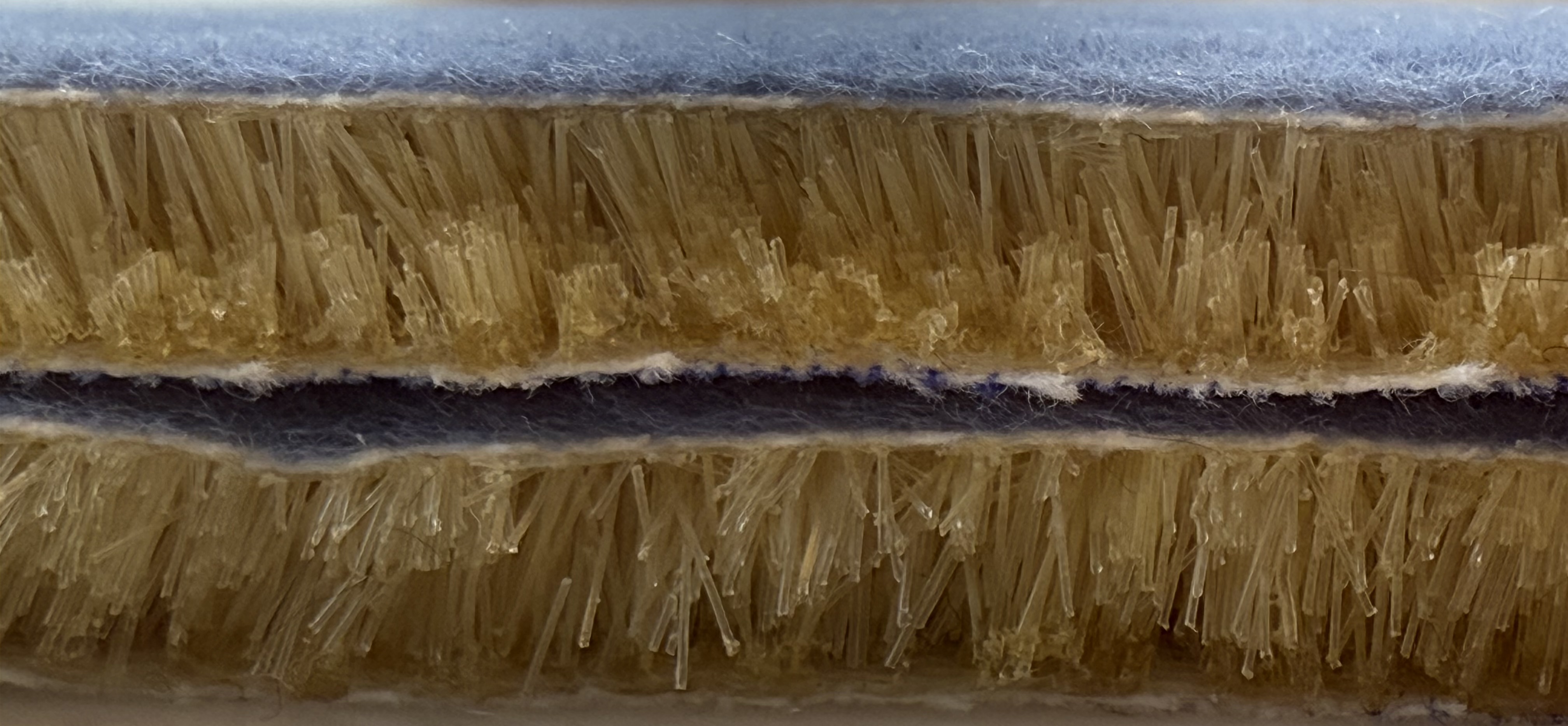
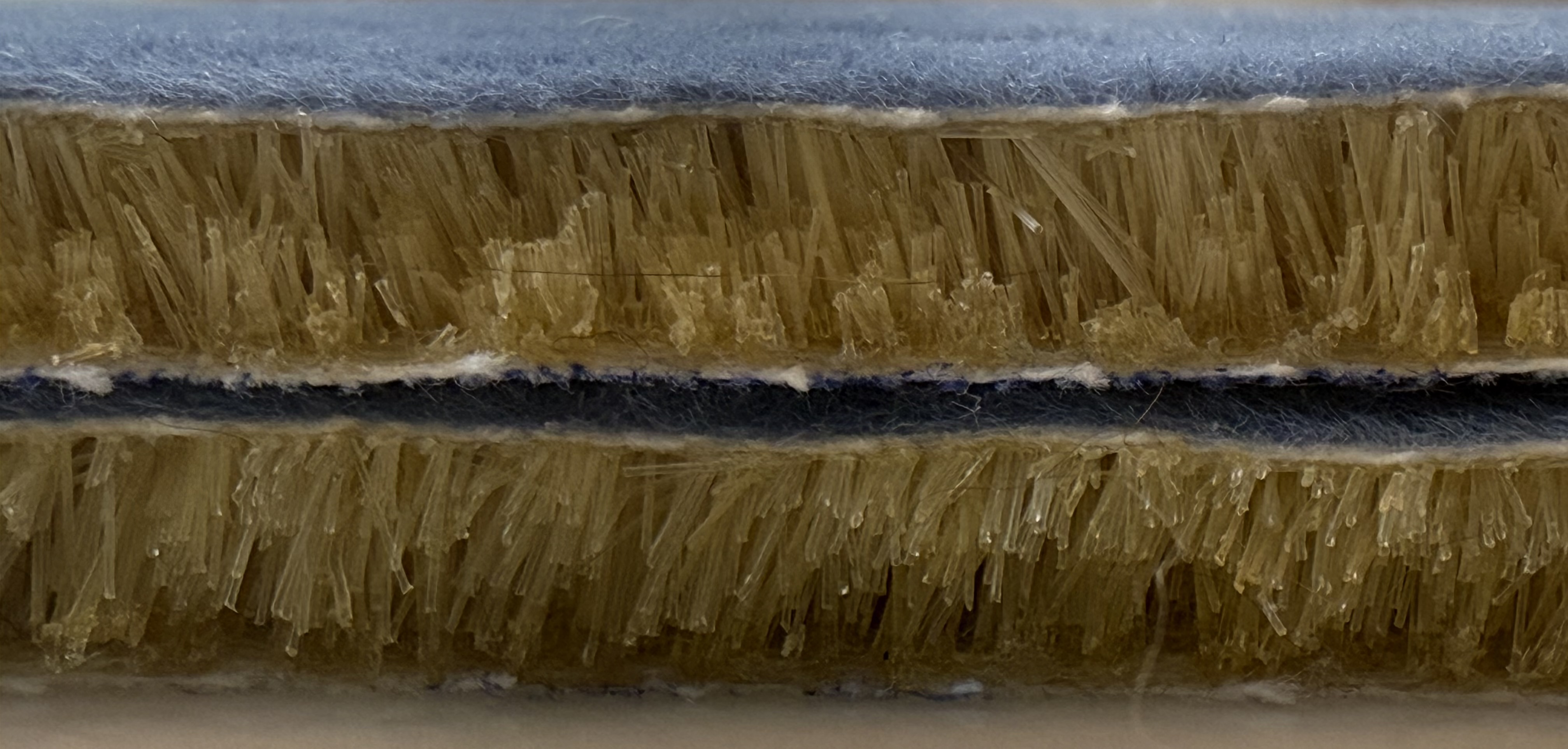
What FEAM is
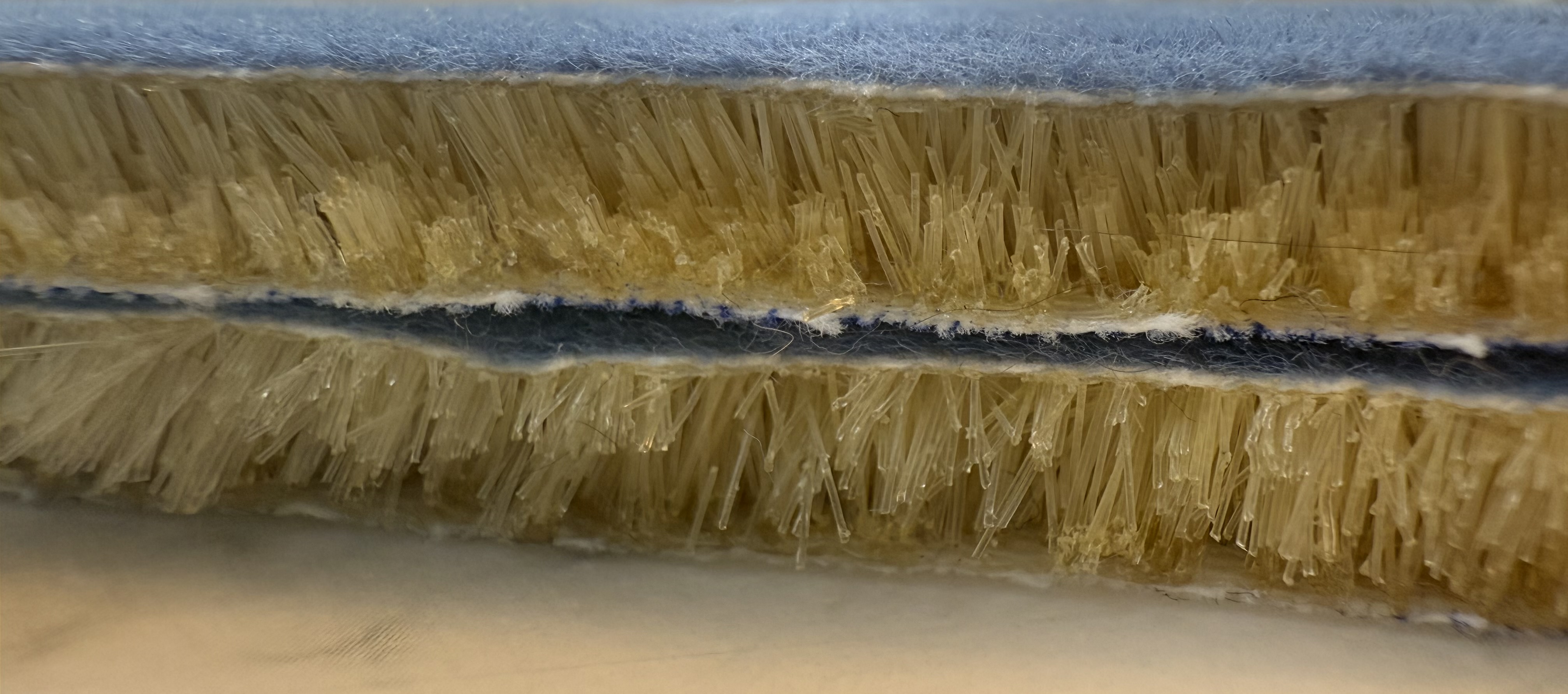
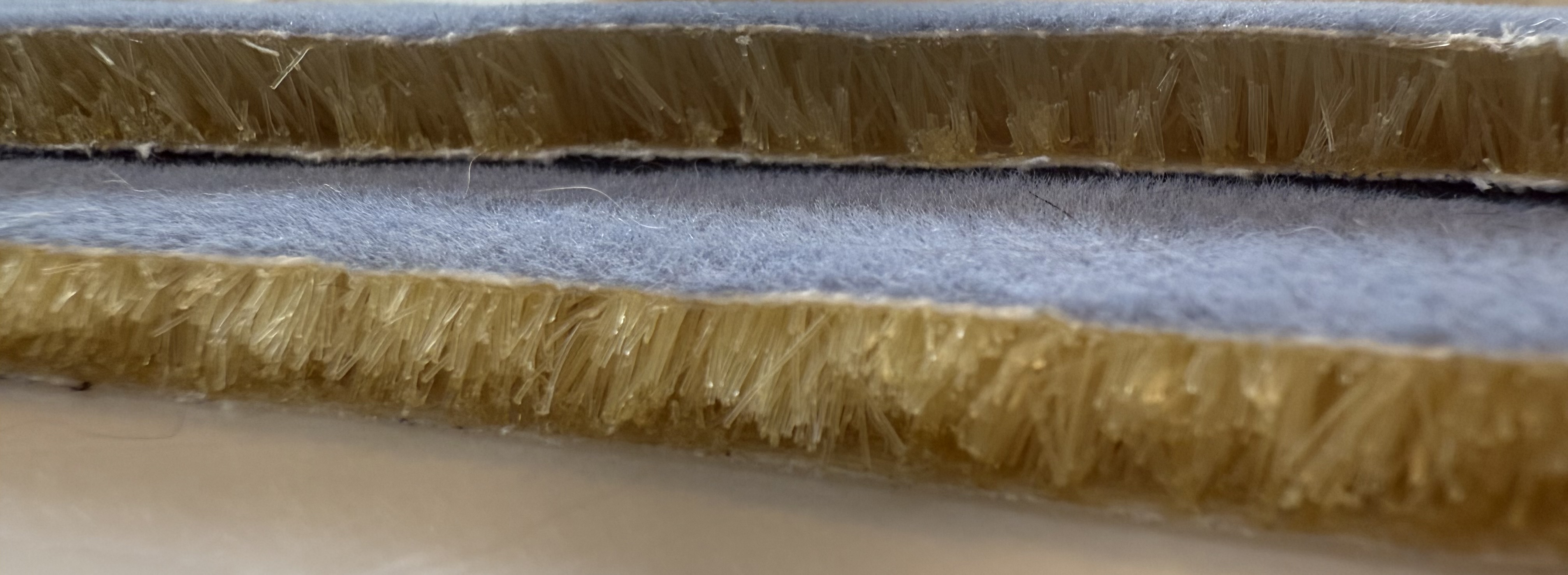
FEAM is a fiber based energy absorbing pad. Short nylon fibers are driven upright into an adhesive coated fabric using an electric field, then two flocked surfaces are brought together to create an interlocking forest of fibers. The result is a thin pad that manages energy under compression and shear. FEAM is protected by utility patents.
How it works
Under load, many fibers bend and recover, while others rub and slide. That mix of buckling and friction spreads incoming energy over time and area, which reduces peak forces and helps manage rotational components that matter in real impacts.
Why it matters
Since the 1960s, foams have handled compression only. Real impacts also involve shear. FEAM’s fiber field is tuned for both, which is why the lab focused on shear loading under realistic pre-compression conditions.
What the lab focused on
The university team studied how fiber diameter, fiber length, and flock density influence energy absorption under impact shear with a controlled pre load. The test setup used guided drop impacts and measured force and displacement to calculate energy density absorbed by the pad.
The findings point to short fibers with smaller diameters at controlled density as a sweet spot for shear energy absorption, with the caveat that clumping reduces performance. These insights guide our quality checks and tuning plan for production.
FEAM Outperforms Foam
In controlled impact shear tests, FEAM absorbed significantly more energy than standard vinyl nitrile foam. The chart below shows
how FEAM continues to manage stress over a larger strain window, while foam peaks quickly and loses protection. More area under
the curve means more energy absorbed and better protection in real-world impacts.
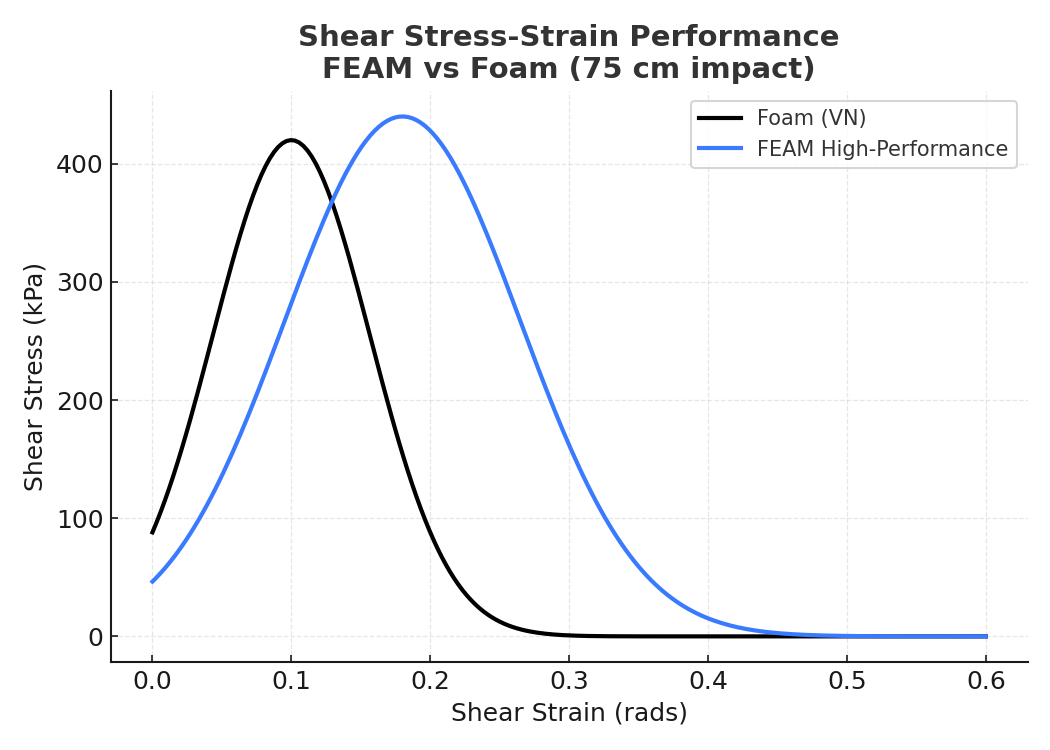
This chart shows high-impact velocity results (75 cm drop height).
There’s also low-impact velocity data available, as well as much more within the many studies that have been conducted on this breakthrough material. To gain access to these documents, get in touch with us by filling out one of our contact forms!